Advanced Cardiac Imaging
- Faculty
- Echocardiography
- Cardiac CT
- Cardiac MR
- Nuclear Cardiology
- Clinical Trials
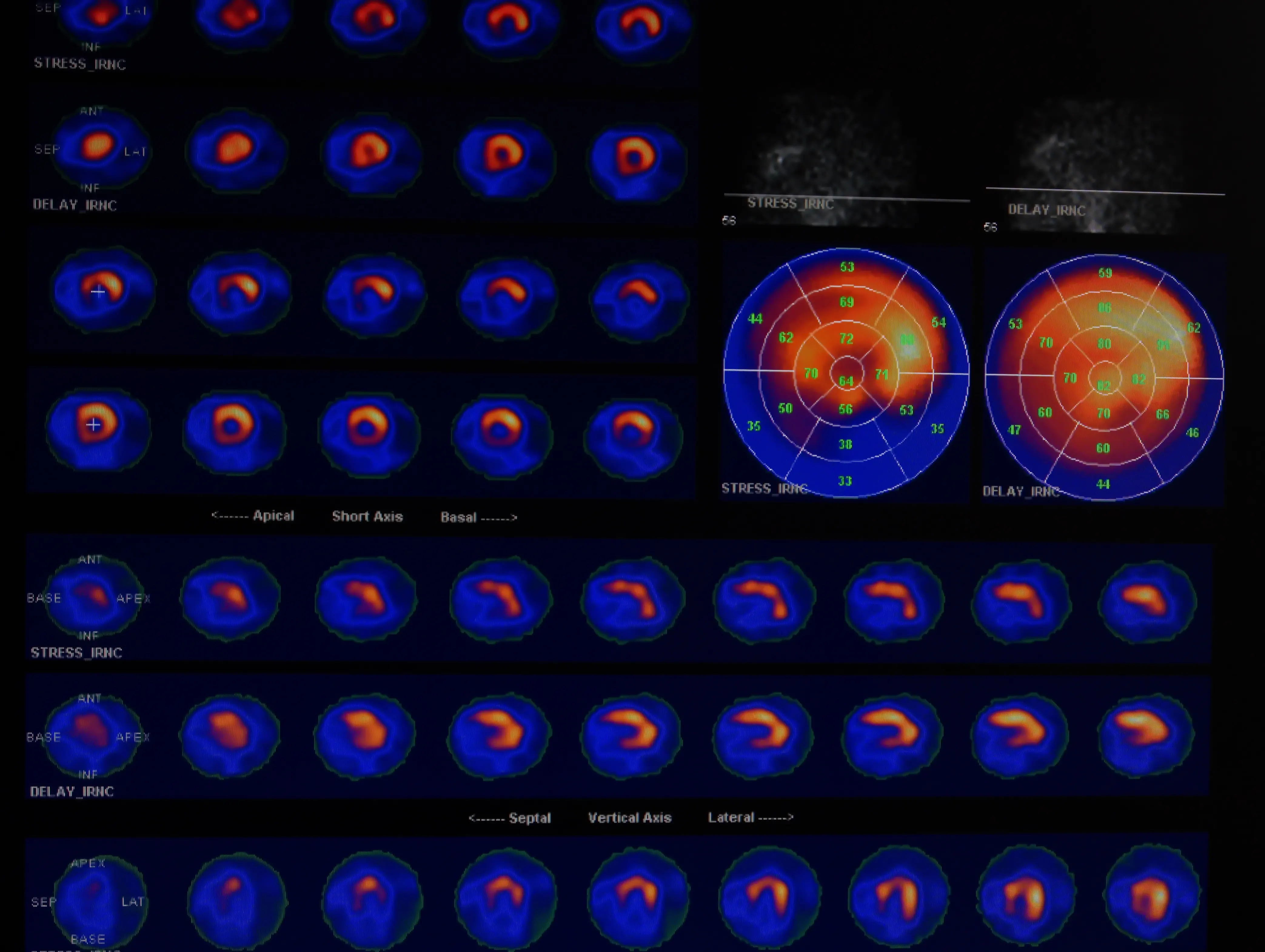 Nuclear cardiology is a specialized field of cardiology that uses small amounts of radioactive substances (radiotracers) to diagnose and evaluate heart conditions.
Nuclear cardiology is a specialized field of cardiology that uses small amounts of radioactive substances (radiotracers) to diagnose and evaluate heart conditions.
Radiotracers are injected into the bloodstream, and special cameras are used to create images of the heart and detect areas of poor blood flow or damage to the heart muscle.
A myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) test uses a radiotracer to evaluate blood flow to the heart muscle during exercise or at rest. Other nuclear cardiology tests include positron emission tomography (PET) scans and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) scans.
Nuclear cardiology tests can help doctors diagnose and evaluate a range of heart conditions, including coronary artery disease, heart attack, and heart failure. They can also be used to assess the effectiveness of treatments and guide decisions about further management.
Although nuclear cardiology tests involve exposure to a small amount of radiation, the benefits of the test generally outweigh the risks for most patients.
