Robert Ross Lab
- Research
- People
- Publications
- Contact
 The long-term goals are to provide novel insights about the mechanisms of normal cardiovascular function and growth, as well as identifying novel therapies for treating heart failure.
The long-term goals are to provide novel insights about the mechanisms of normal cardiovascular function and growth, as well as identifying novel therapies for treating heart failure.
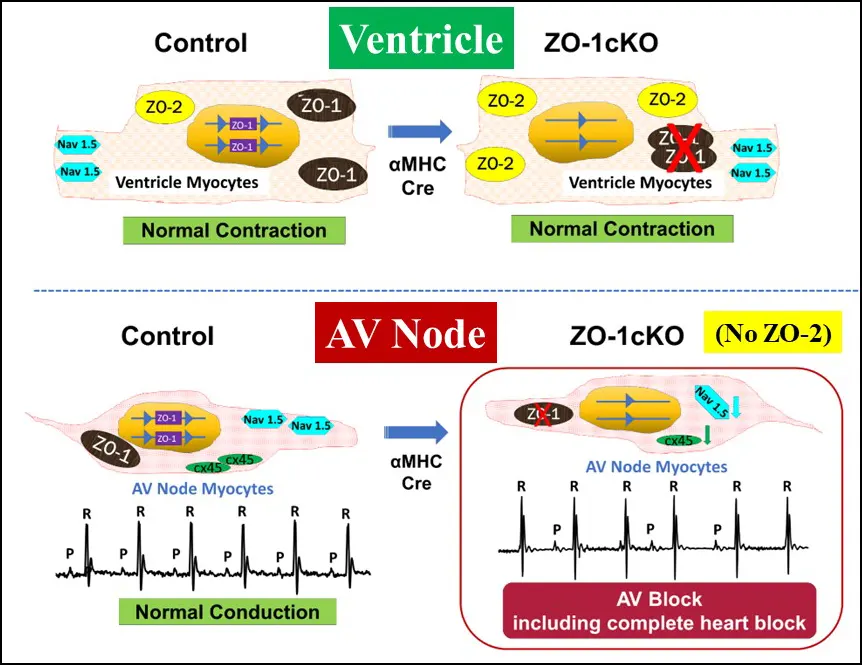
Many of our studies center on proteins are found in the regions of the cardiac muscle cell known as the intercalated disc and costamere. They may play roles in converting mechanical signals to biochemical ones, a process termed mechanotransduction, and also provide structural support for the cell and its sub-cellular components. Investigations are on the role of these proteins in cardiac conduction, rhythm disturbances, growth, remodeling and preservation of normal function. Though rare, variants or mutations in these proteins have been linked to human cardiac disease.
Additional studies in the lab study mitochondrial proteins, and extend some of our work in cardiac muscle, to similar studies in skeletal muscle. For all of these studies, we make extensive use of genetically manipulated mouse models and cells derived from them, in molecular, biochemical and physiological investigations.
